Aso Titers Interpretation
ASO titers remain normal in about 15 of individuals with the disease. 1 ASO Titers aka.
Chapter 31 Common Serological Test Antistreptolysin O Aso C Reactive Protein Crp Labpedia Net
In the area where rheumatic fever or poststreptococcal.
Aso titers interpretation. ASO titer may be interpreted either by comparison of acute and convalescent-phase titers or against reference upper limit of normal values. Elevated ASO titers are found in the sera of about 85 of individuals with rheumatic fever. A rising ASO titer regardless of absolute value is an indication of GABHS strep.
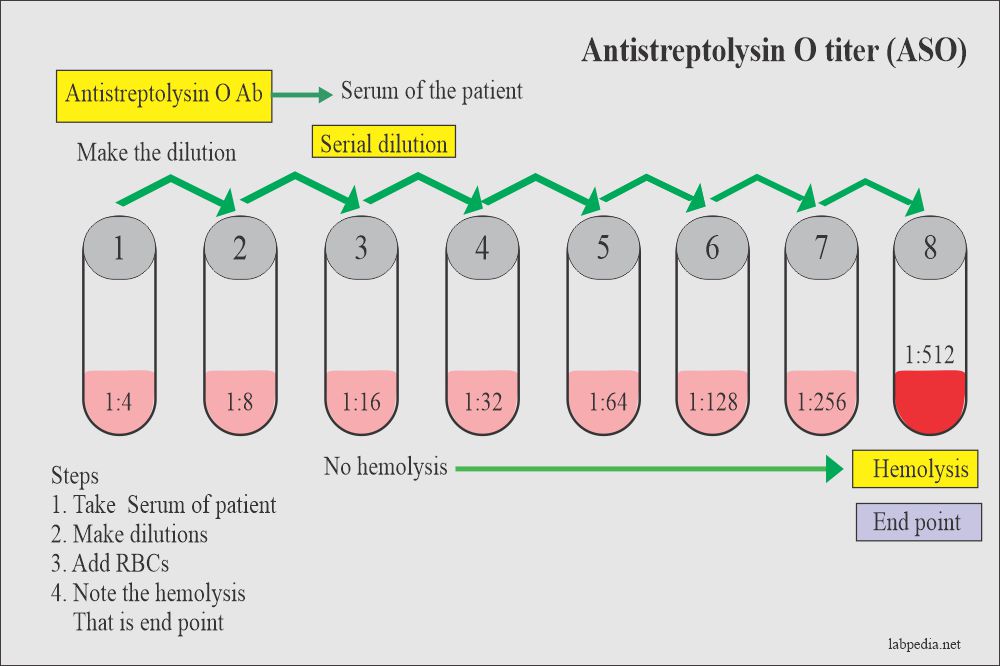
The standard tube dilution method WHO was used for estimating ASO titers. The ASO titer is determined as the highest dilution showing no sign of hemolysis. N Sera with positive results in the qualitative test should be retested in the semi-quantitative test.
Control tube 7 should show no hemolysis and control tube 8 should be completely hemolyzed. However you need a baseline to be sure it is rising. An ASO titer is done to find out if you have a current or recent strep infection that may have caused these health problems.
They may get higher for several weeks before decreasing. The lack of agglutination indicates an ASO level lower than200 IUml in the sample. The higher the result is the more antibody that is present in the blood unless a titer is performed which is a ratio and therefore is interpreted differently.
If there is hemolysis in all tubes. INTERPRETATION OF RESULTS. Although the antistreptolysin O ASO test is quite reliable performing the anti-DNase is justified because ASO response is not universal and elevated ASO titers are found in the sera of about 85 of individuals with rheumatic fever.
Up to 95 of people who are eventually diagnosed with lupus for example have the first step of the diagnostic process be a positive ANA titer blood test. 1112 Since over diagnosis of ARF based on a raised ASOT is not uncommon the ULN value of ASO in normal children is of importance to interpret ASO titers in patients suspected to have ARF. Streptolysin O is a toxin produced by group A.
A falling ASO titer indicates that there was strep but no one knows when. Although the antistreptolysin O ASO test is quite reliable performing the anti-DNase is justified for 2 primary reasons. A positive ANA titer blood test indicates the presence of an autoimmune disease.
This is especially true if a sample taken 10 to 14 days later is also negative low titer of antibody and if an anti-DNase B test is also negative low titer of antibody. A negative ASO or ASO that is present at very low titers means the person tested most likely has not had a recent strep infection. Antibodies from a strep infection begin to increase about 1 week after a strep infection.
Elevated values are consistent with an antecedent infection by group A streptococci. Levels need to be compared to a baseline. N Agglutination indicates an ASO content of more than200 IUml in the specimen.
While a number of tests utilize different antigens of GAS the most frequently performed tests are those that determine the anti-streptolysin O ASO titer and the anti-DNase B ADB titer 8 18. A high ASO titer could be anything including that the titer is falling rising or just a high baseline. It was found that 239 IU was the upper limit of normal in the study population which can be considered as the baseline ASO titer.
200 400 mgdl medical significance may be for IgG antibodies meant by old infection or immunized persons too. Resul Interpretation of ASO Tube Test. Other antibiotics will prevent the ASO titre from rising.
Rise in titer twofold from the acute phase to the convalescent phase is the best evidence of antecedent infection with group A streptococci. The reagent has been adjusted in the way that presence of an ASO titer of 200 IUmL or higher in the serum gives a visible. This can provide useful guidelines for physicians in the interpretation of elevated ASO titers in cases of suspected acute rheumatic fever.
Normal sera has an ASO titer of less than 200 lUml ie reportedly 166-200 lUmL depending on the population. Streptococcal infections and ASO titer values. Understanding Anti-Streptolysin O ASO Titers Author Unknown Anti-streptolysin O is an antibody reaction against against streptococcal toxin left over in the body after a specific strep infection generally Group A Beta-Hemolytic Strep.
ASO titer is a test that measures these antibodies in the blood serum. Antistreptolysin-O ASO titer test results can be reported in several different ways. Greater than 24 mgdl medical significance of positive CRP results in patients serum indicate severity of inflammation.
The ASO titer test measures antibodies produced by your body in response to a toxin known as streptolysin O. Ideally it is recommended that the titer be determined in the acute phase and then determined in the convalescent phase 14 to 28 days later with a positive result defined as. ASO test method is based on an immunological reaction between streptococcal exoenzymes bound to biologically inert latex particles and streptococcal antibodies in the test sample.
The antibodies level starts to rise in 1-3 weeks after streptococcal infection peaks in 3-5 weeks and then goes back to. It is the direction in which the. Compare the agglutination with that of positive and negative control for a correct interpretation.
Then it declines in next 4 to 6 months. First the ASO response is not universal. Upper limit of normal ULN values of ASOT are known to vary also with respect to different geographical locations season and site of infection.
ASO raised titer indicates recent group A streptococcus pharyngitis within the last 2 months. ASO antibody is positive in. Additional testing is usually performed as a follow-up to help determine what specific disease may be present.
However the interpretation is generally the same. Increased titer develops 7 to 14 days after the infection rises rapidly to a peak in 4 to 6 weeks.

Komentar
Posting Komentar